Meet the 16 characters that brought Google’s Chrome to its knees
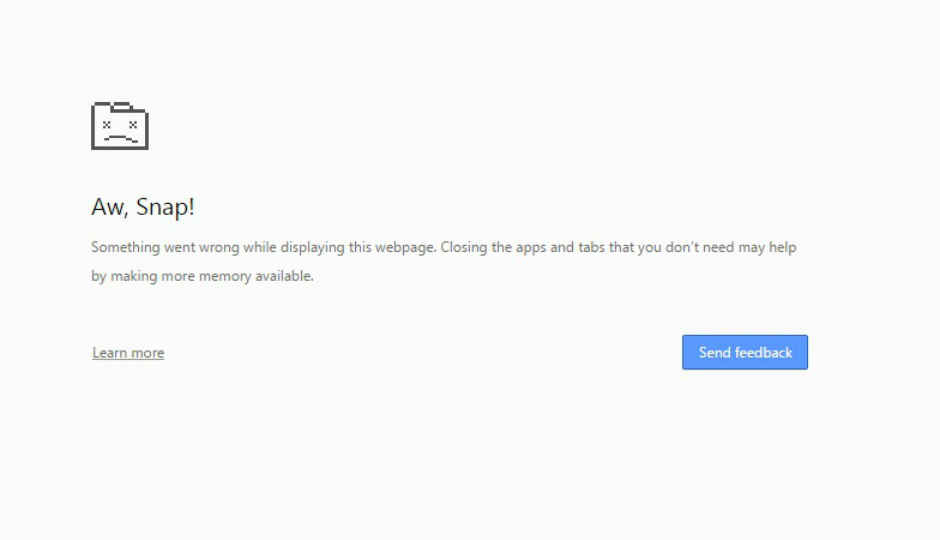
A bug can cause Google Chrome to crash, simply by hovering your mouse over it, or by entering it in the browser’s address field.
A bug, that can cause Google’s Chrome browser to crash, has been discovered. The browser has been seen to crash just by hovering the cursor over the link. The original 26-character long code was found by Andris Atteka, who reported the bug to Google, and blogged about the issue. He said in his blog that Chrome can be crashed by adding a NULL character in the URL string. “Unfortunately no reward was awarded as this was deemed to be only a DOS vulnerability. Anyway, making secure software is much harder than finding issues in it. Thanks Google,” wrote Atteka.
The original code was shortened to 16 characters by Venturebeat. The shorter code can also be copied into the address field of the Google Chrome browser, to crash the entire window. If you want to try it out for yourself, the code is given below. The code has not been hyperlinked, so that your browser does not crash when you accidently hover your mouse over it. The bug doesn’t seem to affect those using Chrome on Mac devices, or the mobile version of Chrome on Android.
http://a/%%30%30
Google announced Chrome v45 earlier this month. The new browser aims to address its issues on exorbitant RAM consumption by making it more power-efficient. This version of Chrome is capable of detecting when a page is idle, and clear up the memory being taken up by it. Google has claimed that the new version has managed to reduce memory usage by upto 10 per cent, and works even better with complex websites – freeing up almost a quarter of memory used by a tab, when Gmail was open on it.
It was also reported that Google Chrome will block all Flash-based ads by default. When a user visits a website with Flash advertisements, it will be paused by default. The user will have an option to manually activate these advertisements to view them. The company also said that only Flash content, that is not central to a page, will be blocked. Google’s reason behind the move is that additional Flash-based content increases a page’s load time, and causes devices to consume more battery power.