HIGHLIGHTS
The network adapter settings have several options that can be tinkered around. We show you how you can make the most of it.
If you’ve ever delved into your Windows network adapter settings, from tweaking IP addresses and DNS gateways to enabling/disabling adapters, you’ve likely touched upon basic configurations. Beyond these basics lie several options that can significantly impact your wired and wireless connections. In this guide, we’ll explore crucial tips to help optimize your network adapter properties for enhanced performance.
Locating the Network Adapter Settings



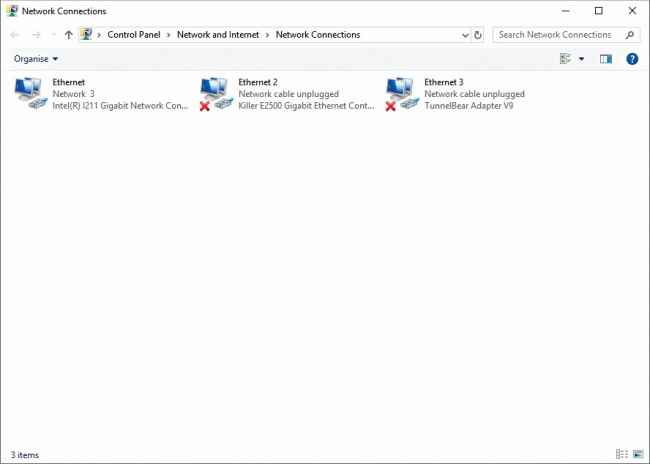
All your network adapters will be listed here
Before diving into the tips, here’s how to access the network adapter properties:
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Ethernet > Change adapter options.
- Remember to modify settings for the active internet connection, whether via Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
Alternate Access Methods:
- Right-click on the Network icon in the system tray > Open Network & Internet Settings.
- Use the Start search menu or press Win + X, then press W for quick access to Network & Internet settings.
Exploring Advanced Network Adapter Settings:
- Receive Buffers: Receive buffers refer to the system memory allocated for storing incoming network data before processing. Adjusting the size of receive buffers impacts the efficiency of packet reception and can affect network performance. Larger buffer sizes generally enhance performance by accommodating more incoming data, reducing the risk of packet loss, and optimizing throughput. However, increasing buffer sizes also consumes more system memory.
- Maximum Supported Speed (EEE Max Support Speed): EEE (Energy-Efficient Ethernet) Max Support Speed pertains to the highest speed supported by the Energy-Efficient Ethernet feature. EEE aims to reduce power consumption during periods of low network activity. Optimizing this setting involves configuring the adapter to operate at the highest supported speed while ensuring energy efficiency during idle or low-traffic periods. This setting can impact both performance and power consumption.
Guidance on Optimizing Network Adapter Settings:
- Receive Buffers (256 or 512): Receive buffers manage incoming network data before processing. Increasing the receive buffer size (e.g., from 256 to 512) can potentially enhance network performance. Impact:
- Performance: Larger buffer sizes (512) can accommodate more incoming data, reducing the risk of packet loss and optimizing throughput.
- Benefits: Improved performance in high-traffic scenarios, minimized latency, and enhanced network stability.
- Speed Optimization: Optimizing speed settings involves selecting the highest feasible speed supported by the network adapter. Impact:
- Performance: Higher speed settings ensure faster data transfer rates, enhancing overall network performance.
- Benefits: Improved efficiency, reduced transfer times, and enhanced responsiveness for data-intensive tasks.
- Ethernet Settings Best Practices: Implementing best practices for Ethernet settings can significantly impact network performance. Consider the following:
- Jumbo Frames: Enabling Jumbo Frames (if supported across devices) can reduce overhead and increase data transmission efficiency.
- Flow Control: Configure Flow Control settings for efficient traffic regulation and congestion prevention.
- Receive Side Scaling (RSS): Enable RSS to distribute data processing across multiple CPU cores, enhancing performance for systems with multiple processors.
- Interrupt Moderation: Adjust interrupt moderation to balance CPU utilization and packet handling responsiveness.
- Buffer Sizes: Optimize receive and transmit buffer sizes based on available system memory to prevent packet loss while maximizing performance.
Best Practices Impact:
- Improved Throughput: Enhanced data transfer rates and increased network efficiency.
- Reduced Latency: Minimized delays in data transmission and improved responsiveness.
- Stability and Reliability: Ensured network stability and reduced the risk of data loss or interruptions.
Implementation Notes:
- Consider Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with network devices before making significant changes.
- Test and Monitor: Implement changes gradually, testing performance improvements, and monitoring network behavior to ensure stability.
Optimizing network adapter settings involves a balance between performance enhancements and compatibility. Implementing these adjustments can notably enhance network speed, reliability, and overall performance.
Comparison and Recommendations for Network Adapter Settings:
1) Receive Buffers (256 vs. 512):
- 256 Buffers: Pros – Lower memory usage, suitable for moderate traffic. Cons – Increased risk of packet loss in high-traffic scenarios.
- 512 Buffers: Pros – Reduced packet loss, better performance in high-traffic environments. Cons – Higher memory usage.
Recommendation: For faster internet or maximum performance in demanding network environments, setting receive buffers to 512 is advisable. It provides improved stability and throughput, especially in scenarios with heavy data transfer requirements.
2) Speed Optimization (Auto-Negotiation vs. Manual Selection):
- Auto-Negotiation: Pros – Convenient, adapts to the highest supported speed. Cons – May not always select the maximum available speed.
- Manual Selection: Pros – Ensures maximum available speed. Cons – May cause connectivity issues if set higher than the network supports.
Recommendation: For achieving maximum performance, manually select the highest supported speed to ensure optimal data transfer rates, particularly in scenarios where high-speed connectivity is crucial.
3) Ethernet Settings (Jumbo Frames, Flow Control, RSS, Interrupt Moderation, Buffer Sizes):
- Jumbo Frames: Pros – Increased efficiency, reduced overhead. Cons – Requires consistent support across network devices.
- Flow Control: Pros – Efficient traffic regulation. Cons – Configuration may vary in effectiveness across adapters.
- RSS: Pros – Enhanced CPU utilization for multi-core systems. Cons – May not yield significant improvements on single-core systems.
- Interrupt Moderation: Pros – Optimizes CPU usage. Cons – May impact packet handling responsiveness.
- Buffer Sizes: Pros – Minimized packet loss, improved performance. Cons – Increased memory consumption.
Recommendation: For maximum performance, configure Ethernet settings cautiously. Enable Jumbo Frames if uniformly supported, fine-tune Flow Control, utilize RSS on multi-core systems, balance Interrupt Moderation for CPU usage, and optimize buffer sizes based on memory availability.


4) Scenario-based Recommendations:
- For Faster Internet: Increase receive buffers to 512, manually select maximum supported speed, and fine-tune Ethernet settings for efficiency.
- For Maximum Performance: Implement advanced configurations, including Jumbo Frames, optimized Flow Control, RSS for multi-core systems, and carefully adjusted buffer sizes to balance performance and memory usage.
Resetting Network in Case of Issues:
If you experience connectivity problems resulting from recent changes made to your network settings, you can perform a network reset to revert settings to their default state. Follow these steps:
- Open Network Settings: Go to your computer’s settings and select “Network & Internet.”
- Access Network Status: Within the “Network & Internet” settings, navigate to the “Status” tab.
- Find Network Reset Option: Look for the “Network Reset” option within the “Status” section. It’s usually located towards the bottom of the page.
- Initiate Network Reset: Click on the “Network Reset” option. A confirmation prompt may appear, informing you that resetting the network will remove and reinstall all network adapters and set other network components back to their original settings.
- Confirm the Reset: Confirm the action to proceed with the network reset. Note that this process might take a few moments to complete.
- Restart Your Device: After the network reset is executed, restart your device to allow the changes to take effect.
- Reconnect to Networks: Once your device restarts, reconnect to your preferred Wi-Fi or Ethernet networks. You may need to re-enter Wi-Fi passwords or reconnect to your Ethernet network, depending on your setup.
- Test Connectivity: Check your internet connectivity and ensure that the network-related issues have been resolved.
- Performing a network reset is a convenient way to troubleshoot and resolve connectivity issues caused by recent changes in network settings. However, keep in mind that this action will reset all network-related configurations to their default settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why should I adjust network adapter settings?
Fine-tuning network adapter settings can optimize network performance, improve stability, and cater to specific connectivity requirements.
- Are there risks associated with tweaking Ethernet settings like Jumbo Frames or Interrupt Moderation?
While these settings can improve performance, they may require consistent support across devices and could potentially affect compatibility.
- What should I do if my network settings reset doesn’t resolve the issue?
Check router settings, restart devices, or contact your internet service provider (ISP) for further assistance if the network reset doesn’t resolve the problem.
- Is it safe to disable certain network adapter settings for better performance?
Disabling features like Flow Control or Interrupt Moderation might enhance efficiency but could impact certain connections. It’s advisable to research and understand these settings before disabling them.
- How do I test if my network changes have improved performance?
Run speed tests or monitor network performance using relevant software to assess improvements resulting from adjusted settings.
- Can I apply network adapter settings changes on any device?
Settings may vary based on the device and the specific network adapter. Ensure compatibility and research before applying changes, especially on different device models or operating systems.
- What if I’m unsure about adjusting network settings?
If uncertain, consult technical support or professional assistance before making significant changes to network adapter settings to avoid potential issues or complications.
Conclusion
Fine-tuning network adapter settings is pivotal for optimal network performance. Adjustments in settings like Receive Buffers, Speed Optimization, and Ethernet configurations can greatly impact stability and connectivity. In case of connectivity issues arising from changes, don’t hesitate to utilize the “Network Reset” option for swift troubleshooting.
Should you require personalized assistance or encounter persistent issues, seek guidance from networking professionals or technical support teams. Their expertise can provide tailored solutions to optimize your network settings effectively.
Ensure a smoother network experience by staying informed and making informed adjustments to your network settings.