Cybersecurity 101: Common cyber threats and online safety concepts explained

In today’s interconnected world, the internet has become an integral part of our daily lives. From socializing and shopping to banking and working, digital platforms facilitate a multitude of activities. However, this digital convenience also comes with significant risks. Online safety isn’t just about protecting your computer from viruses anymore – it’s about safeguarding your identity, privacy, and financial well-being in a landscape where cyber threats are constantly evolving.
 Survey
SurveyAlso read: AI impact on cyber security future: The good, bad and ugly
This article lays the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of online safety, emphasizing the importance of digital security and unveiling the common threats that lurk in the cyber world.
Cybersecurity matters: Why online safety is important
The digital age has ushered in unprecedented convenience and connectivity, but it has also opened the door to a myriad of security risks. Cybercrimes, ranging from identity theft to financial fraud, are on the rise, with millions of people falling victim each year.
The consequences can be devastating, leading to loss of privacy, significant financial setbacks, and long-term damage to one’s digital and real-world reputation.
Cybersecurity Ventures predicted that cybercrime damages might reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, signaling an urgent need for individuals to take their digital safety seriously. This alarming statistic is a wakeup call highlighting the critical need for proactive measures in online safety.
Key concepts in cybersecurity
Before delving into specific threats and protection strategies, it’s essential to understand the basic principles of digital security:

1) Encryption
This is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. Understanding encryption is crucial for activities such as sending confidential emails or securely accessing websites.
2) Authentication
This refers to the methods used to verify the identity of a user, application, or device. Familiar examples include passwords, biometric scans, and two-factor authentication (2FA).
3) Secure Networks
These are networks that have been fortified against unauthorized access. It’s important to use secure connections, such as those provided by VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), especially when accessing the internet over public Wi-Fi.
By grasping these concepts, you equip yourself with the knowledge to navigate the online world more safely, understanding how your data is protected and what measures you can take to enhance that protection.
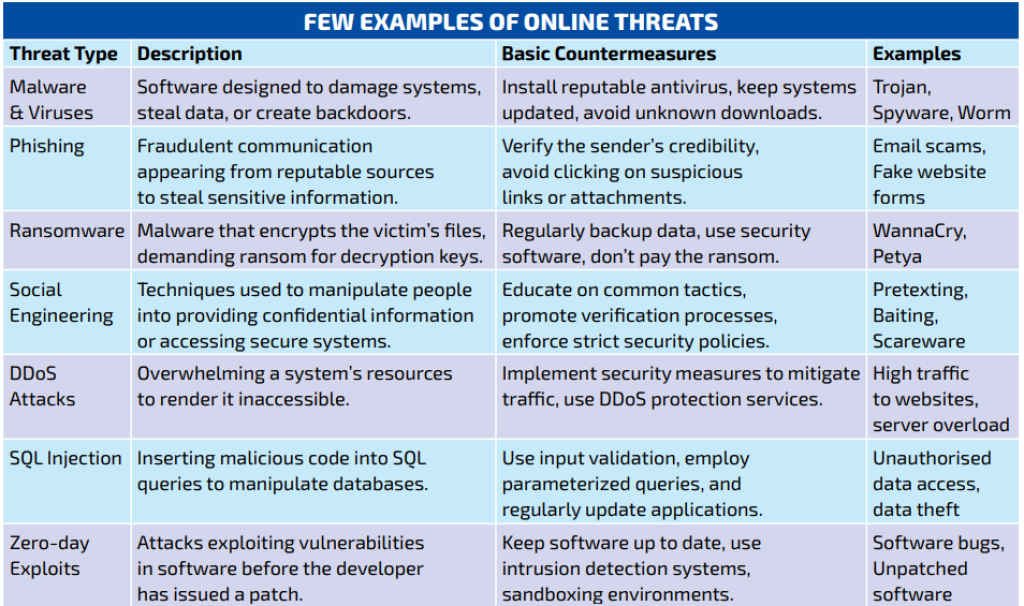
Common cyber threats and how they work
Awareness is the first step toward protection. Here are the most prevalent online threats that average people fall prey to unsuspectingly, providing you with the insight needed to identify and avoid them.
Also read: This Android malware can steal your OTPs, record your screen, and more: Is your phone safe?
1) Malware: Viruses, Spyware, Trojan Horses
Malware (malicious software) is an umbrella term encompassing various software designed to inflict harm on a user’s system. Common malware types include:
- Viruses: Self-replicating programs that spread from one device to another, often infecting files or programs. They can steal data, corrupt files, or disrupt system functions.
- Spyware: Covertly monitors user activity, capturing data like keystrokes, browsing history, and even financial information.
- Trojan Horses: Disguised as legitimate software, they trick users into installing them. Once installed, they can steal information, download other malware, or damage the system.

Signs of malware infection may include:
- Unusual system slowdowns or crashes.
- Unexplained pop-up ads or changes to your browser settings.
- Unknown programs running in the background.
- Important files or data disappearing.
2) Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing is a deceptive attempt to lure users into revealing personal information or clicking malicious links. Phishing emails or messages often:
- Appear to be from legitimate sources: Banks, social media platforms, or even trusted colleagues.
- Create a sense of urgency: Threatening account suspension, requesting immediate action, or highlighting a “limited-time offer.”
- Contain links that lead to fake websites: Designed to steal login credentials, financial information, or infect the device with malware.
Social engineering exploits human psychology to manipulate individuals into compromising security measures. Common tactics include:
- Pretexting: Creating a false scenario to gain trust and access to personal information.
- Baiting: Luring users with irresistible offers or exploiting their curiosity to click malicious links or attachments.
- Quid pro quo: Offering seemingly helpful solutions in exchange for sensitive information.
Combating Phishing and Social Engineering:
- Be cautious of unsolicited emails or messages: Do not click on links or attachments from unknown senders.
- Verify the sender’s identity: Contact the supposed sender through a trusted channel to confirm the legitimacy of the communication.
- Be wary of urgency or emotional manipulation: Do not rush into any actions based on pressure tactics.
- Value your data: Never share personal information through email or unverified websites.

3) Ransomware
Ransomware is a particularly disruptive form of malware that encrypts a user’s files, rendering them inaccessible. The attacker then demands a ransom payment, typically in cryptocurrency, for the decryption key.
Also read: Ransomware attacks have reportedly surged to over 1.2 million a month: Who are all affected?
Impacts of ransomware:
- Victims can lose access to critical data like photos, documents, and business files.
- Businesses face operational disruptions and potential financial losses.
Preventing Ransomware Attacks:
- Regular backups: Ensure you have a recent, uninfected copy of your important data stored securely offline.
- Software updates: Keep your operating system, applications, and security software up-to-date to address vulnerabilities.
- Exercise caution with attachments and links: Do not open suspicious emails or click on links from unknown senders.
Online safety and cybersecurity is a multifaceted challenge that requires awareness and proactive measures. By understanding the importance of online safety, familiarizing yourself with key digital security concepts, and recognizing common cyber threats, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to cybercrime. Stay informed, stay cautious, and take control of your digital life.
Also read: Quick Heal’s Vishal Salvi on fighting malware to keep India cyber safe
Team Digit
Team Digit is made up of some of the most experienced and geekiest technology editors in India! View Full Profile